댓글 쓰기 권한이 없습니다. 로그인 하시겠습니까?
Development of an Autothermal Formate-Based Hydrogen Generator: From Optimization of Formate Dehydrogenation Conditions to Thermal Integration with Fuel Cells
| Journal | ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. |
|---|---|
| Author | Yeon Jin Hwang, Yearang Kwon, Yongmin Kim, Hyuntae Sohn, Suk Woo Nam, Joohoon Kim, Tom Autrey, Chang Won Yoon, Young Suk Jo, and Hyangsoo Jeong |
| Citation | ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 26, 9846?9856 |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c02775 |
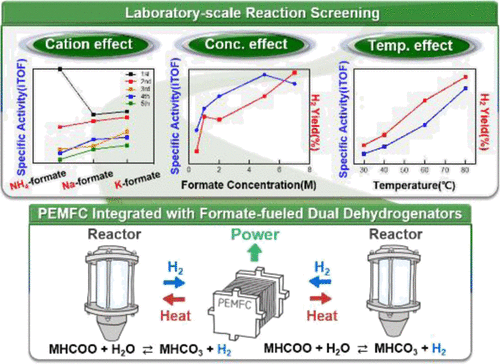
Formate received significant attention for storing H2 in chemical bonds using the concept of H2 carriers. In this report, hydrogen generation from formate was optimized systematically by varying reaction variables. Initial mass activity with a turnover frequency of 3200 molH2 molPd?1 h?1 and 92% H2 yield were obtained in sodium formate (7 M 2.0 mL) dehydrogenation over Pd(3 wt %)/C at 80 °C. Influence of formate cations (Na, K, and NH4) on dehydrogenation was also elucidated, presenting that the fastest initial reaction kinetics was achieved with ammonium formate, whereas the highest H2 yield was obtained with potassium formate (PF) in multiple catalyst recycle tests. Finally, an on-site power generation system was integrated, where a proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) was operated in conjunction with H2 produced from the custom developed semibatch dehydrogenation reactors. The system operation was demonstrated with continuous feeding of PF to generate H2 and power on demand without an external heat source by utilizing waste heat produced from the PEMFC in a highly efficient manner.
-
Read More

Electrochemiluminescence of Glutathione?Stabilized Au Nanoclusters Fractionated by Gel Electrophoresis in Water
Category2020 AuthorYunjeong Kang, Joohoon Kim JournalChemElectroChem CitationChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 1092?1096
-
Read More

Composition-dependent catalytic activity of bimetallic PtPd dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles having an average size of 1.7 nm for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane
Category2020 AuthorYoungwon Ju, Joohoon Kim JournalKorean J. Chem. Eng. CitationKorean J. Chem. Eng., 37(8), 1387-1393 (2020)
-
Read More

Development of an Autothermal Formate-Based Hydrogen Generator: From Optimization of Formate Dehydrogenation Conditions to Thermal Integration with Fuel Cells
Category2020 AuthorYeon Jin Hwang, Yearang Kwon, Yongmin Kim, Hyuntae Sohn, Suk Woo Nam, Joohoon Kim, Tom Autrey, Chang Won Yoon, Young Suk Jo, and Hyangsoo Jeong JournalACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. CitationACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 26, 9846?9856
Designed by sketchbooks.co.kr / sketchbook5 board skin
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
.png)


 Composition-dependent catalytic activity of bimetalli...
Composition-dependent catalytic activity of bimetalli...