댓글 쓰기 권한이 없습니다. 로그인 하시겠습니까?
Repetitively Coupled Chemical Reduction and Galvanic Exchange as a Synthesis Strategy for Expanding Applicable Number of Pt Atoms in Dendrimer-Encapsulated Pt Nanoparticles
| Journal | Langmuir |
|---|---|
| Author | Taehoon Cho, Changwon Yoon, Joohoon KIM |
| Citation | Langmuir 34, 25, 7436-7444 |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01169 |
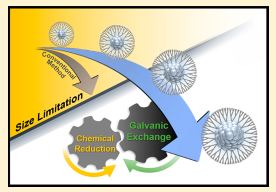
: In this study, we report the controllable synthesis of
dendrimer-encapsulated Pt nanoparticles (Pt DENs) utilizing repetitively
coupled chemical reduction and galvanic exchange reactions. The synthesis
strategy allows the expansion of the applicable number of Pt atoms
encapsulated inside dendrimers to more than 1000 without being limited
by the fixed number of complexation sites for Pt2+ precursor ions in the
dendrimers. The synthesis of Pt DENs is achieved in a short period of time
(i.e., ∼10 min) simply by the coaddition of appropriate amounts of Cu2+
and Pt2+ precursors into aqueous dendrimer solution and subsequent
addition of reducing agents such as BH4
?, resulting in fast and selective
complexation of Cu2+ with the dendrimers and subsequent chemical
reduction of the complexed Cu2+ while uncomplexed Pt2+ precursors
remain oxidized. Interestingly, the chemical reduction of Cu2+, leading to
the formation of Cu nanoparticles encapsulated inside the dendrimers, is
coupled with the galvanic exchange of the Cu nanoparticles with the nearby Pt2+. This coupling repetitively proceeds until all of
the added Pt2+ ions form into Pt nanoparticles encapsulated inside the dendrimers. In contrast to the conventional method
utilizing direct chemical reduction, this repetitively coupled chemical reduction and galvanic exchange enables a substantial
increase in the applicable number of Pt atoms up to 1320 in Pt DENs while maintaining the unique features of DENs.
-
Read More
Electrochemical Functionalization of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Amine-Terminated Dendrimers Encapsulating Pt Nanoparticles: Toward Facile Field-Effect Transistor-Based Sensing Platforms
Category2018 AuthorLee, Chang-Seuk; Ju, Youngwon; Kim, Joohoon; Kim, Tae Hyun JournalSensors and Actuators, B: Chemical CitationSensors and Actuators, B: Chemical Volume275 Pages367-372
-
Read More
Blue Photoluminescence of Au Nanoclusters Synthesized Using Dendrimer Templates under Mild Conditions
Category2018 AuthorJun Myung Kim Hyeong Seop Shim Jihye Kwon Hai Dong Kim Jae Kyu Song Joohoon Kim JournalBULLETIN OF THE KOREAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY CitationBull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2018, Vol. 39, 1324?1327
-
Read More
Feasibility study for combination of ?eld-?ow fractionation(FFF)-based separation of size-coded particle probes with ampli?ed surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) tagging for simultaneous detection of multiple miRNAs
Category2018 AuthorKayeong Shin, Jaeyeong Choi, Yeoju Kim, Yoonjeong Lee, Joohoon Kim, Seungho Lee,, Hoeil Chung JournalJournal of Chromatography A CitationJ .Chromatogr. A 1556(2018) 97?102
-
Read More

Near-infrared electrochemiluminescence from orange fluorescent Au nanoclusters in water
Category2018 AuthorJun Myung Kim, Seonghyun Jeong, Jae Kyu Song, Joohoon Kim JournalChemical Communications CitationChem. Commun., 2018, 54, 2838
-
Read More
Repetitively Coupled Chemical Reduction and Galvanic Exchange as a Synthesis Strategy for Expanding Applicable Number of Pt Atoms in Dendrimer-Encapsulated Pt Nanoparticles
Category2018 AuthorTaehoon Cho, Changwon Yoon, Joohoon KIM JournalLangmuir CitationLangmuir 34, 25, 7436-7444
Designed by sketchbooks.co.kr / sketchbook5 board skin
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
.png)


 Near-infrared electrochemiluminescence from orange fl...
Near-infrared electrochemiluminescence from orange fl...