댓글 쓰기 권한이 없습니다. 로그인 하시겠습니까?
Fluorescence Quenching of Dendrimer-Encapsulated CdS Quantum Dots for the Detection of H2O2
| Journal | Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. |
|---|---|
| Author | Hyojung Lim, Hai Dong Kim, Joohoon Kim |
| Citation | Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2016, 37, 254?257 |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1002/bkcs.10655 |
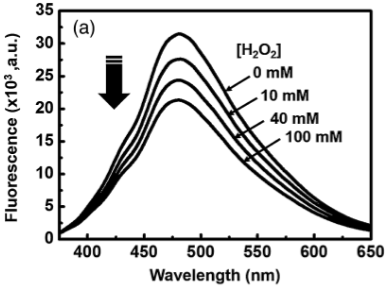
Here, we report H2O2-sensitive fluorescence of CdS QDs encapsulated inside amine-terminated sixth-generation polyamidoamine dendrimers (G6-NH2), which we utilized for the detection of H2O2. Specifically, we synthesized a set of CdS QDs with different structural and optical properties by adjusting the molar ratios (i.e., n = Cd2+/G6-NH2) between Cd2+ ions and G6-NH2 dendrimers. As the Cd2+/G6-NH2 ratio (n) increases from 16 to 128, the size of the resulting CdS QDs increases, as was confirmed by UV?Vis spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Importantly, the CdS QD with the Cd2+/G6-NH2ratio (n) of 64 exhibited significant fluorescence quenching in the presence of H2O2 as well as the strongest fluorescence among the set of CdS QDs. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of the H2O2-sensitive fluorescence of the dendrimer-encapsulated CdS QDs, which enables the use of the CdS QD (n = 64) as a fluorescent reporter for the analysis of H2O2.
-
Read More
Tailoring Catalytic Activity of Pt Nanoparticles Encapsulated Inside Dendrimers by Tuning Nanoparticle Sizes with Subnanometer Accuracy for Sensitive Chemiluminescence-Based Analyses
Category2016 AuthorHyojung Lim, Youngwon Ju, and Joohoon Kim JournalAnal. Chem. CitationAnal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9, 4751?4758
-
Read More
Sensitive Electrochemical Penicillin Sensor Based on Screen-printed Carbon Electrode Modified with Dendrimer-encapsulated Pt Nanoparticles
Category2016 AuthorYoungwon Ju and Joohoon Kim JournalBull. Korean Chem. Soc. CitationBull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2016, 37, 397?400
-
Read More

Fluorescence Quenching of Dendrimer-Encapsulated CdS Quantum Dots for the Detection of H2O2
Category2016 AuthorHyojung Lim, Hai Dong Kim, Joohoon Kim JournalBull. Korean Chem. Soc. CitationBull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2016, 37, 254?257
-
Read More
Functionalization of indium tin oxide electrode with both of dendrimer-encapsulated Pt nanoparticles and chemically converted graphenes for enhanced electrochemiluminescence of luminol/H2O2
Category2016 AuthorJisoo Yoon, Taehoon Cho, Hyojung Lim, Joohoon Kim JournalAnal Bioanal Chem CitationAnal Bioanal Chem (2016) 408:7165?7172
Designed by sketchbooks.co.kr / sketchbook5 board skin
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
.png)


 Sensitive Electrochemical Penicillin Sensor Based ...
Sensitive Electrochemical Penicillin Sensor Based ...
 Functionalization of indium tin oxide electrode w...
Functionalization of indium tin oxide electrode w...