Photoluminescent and Electrochemiluminescent Detection of Fe3+ Using Cyclometalated Iridium Complexes via Fe3+-Catalyzed Hydrolysis
| Journal | Chemistry an Asian journal |
|---|---|
| Author | Hyun Seung No, Minhee Sim, Ik-Soo Shin, Joohoon Kim, Jong-In Hong |
| Citation | Chem. Asian J. 2024, e202400805 |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.202400805 |
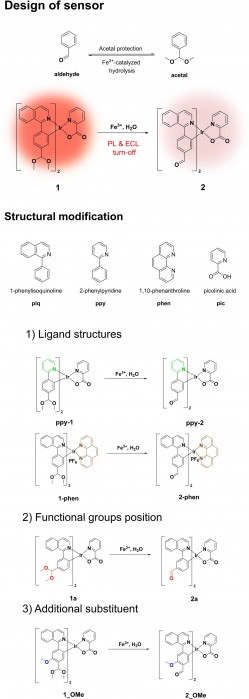
Ferric ion (Fe3+) is a biologically abundant and important metal ion. We developed several cyclometalated iridium complex-based molecular sensors (1, ppy-1, 1-phen, 1?a, and 1_OMe) for the detection of Fe3+ using an acetal moiety as the reaction site. The acetal moiety in iridium complexes undergoes Fe3+-catalyzed hydrolysis and subsequent formation of a formyl group, resulting in turn-off photoluminescent and electrochemiluminescent responses. Sensor 1 showed excellent selectivity toward Fe3+ over other biologically important metal ions. Furthermore, we compared the performance of the sensors based on the structural differences of the iridium complexes, and revealed a relationship between the structure and chemical properties through electrochemical experiments and computational calculations.
Articles
-
 Hybridization of DNA to bead-immobilized probes confined within ...
Hybridization of DNA to bead-immobilized probes confined within ...
-
 Transfer of surface polymerase reaction products to a secondary platf...
Transfer of surface polymerase reaction products to a secondary platf...
-
 Replication of DNA microarrays from zip code masters
Replication of DNA microarrays from zip code masters
-
 Parallel fabrication of RNA microarrays by mechanical transfer from ...
Parallel fabrication of RNA microarrays by mechanical transfer from ...
-
 Replication of DNA microarrays prepared by in situ oligonucleotide ...
Replication of DNA microarrays prepared by in situ oligonucleotide ...
Designed by sketchbooks.co.kr / sketchbook5 board skin
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5
Sketchbook5, 스케치북5